Wind speed measurement is a critical aspect of various industries, ranging from aviation to renewable energy. Wind speed measurement is crucial for various reasons, including assessing potential risks, optimizing energy production, and ensuring safe working conditions in different industries.In this article, we delve into the methods, instruments, and importance of measuring wind speed in professional settings.
Applications of wind speed
The data obtained from wind speed measurements are utilized in industries such as aviation, renewable energy, construction, and agriculture to make informed decisions and mitigate potential hazards.
What is wind speed
Wind speed refers to the rate at which air moves horizontally past a fixed point and is typically measured in meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), or knots.
Units of measurement
Different units are used to express wind speed, with the most common being meters per second (m/s) in scientific contexts and kilometers per hour (km/h) in everyday use.
Factors affecting wind speed
Various factors, including geographic location, topography, and atmospheric conditions, influence wind speed, making it a dynamic parameter to measure accurately.
Instruments for Measuring Wind Speed
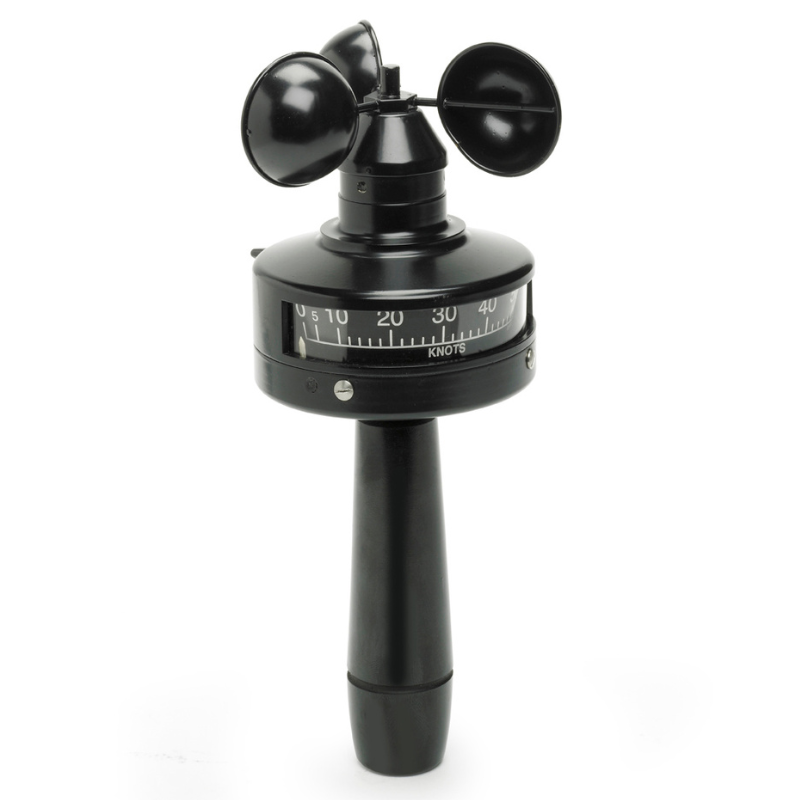
A. Anemometers
Anemometers are the most widely used instruments for measuring wind speed and come in various designs, including cup, vane, and sonic types.

B. Cup anemometers
Cup anemometers consist of rotating cups that capture wind energy, with the rotation speed directly proportional to wind speed.
C. Sonic anemometers
Sonic anemometers utilize ultrasonic signals to measure wind speed and direction accurately and are commonly used in research and meteorological applications.
D. Wind vanes
Wind vanes are instruments used to determine wind direction and are often paired with anemometers to provide comprehensive wind data.
Methods of Measuring Wind Speed
- Direct measurement
Direct measurement involves using instruments such as anemometers to directly assess wind speed at a specific location.
- Indirect measurement
Indirect measurement methods, such as pressure-based techniques, estimate wind speed based on secondary parameters like air pressure differentials.
- Remote sensing techniques
Remote sensing techniques, including satellite imagery and Doppler radar, allow for the measurement of wind speed over large geographic areas without the need for on-site instrumentation.
Accuracy and Precision in Wind Speed Measurement
- Factors influencing accuracy
Factors such as instrument calibration, environmental conditions, and measurement errors can affect the accuracy of wind speed measurements.
- Calibration of instruments
Regular calibration of instruments is essential to maintain accuracy and reliability in wind speed measurement systems.
Importance of precision in professional applications
In professional settings, precise wind speed measurements are crucial for optimizing operations, ensuring safety, and complying with regulatory standards.
Importance in Various Industries
- Aviation
Accurate wind speed data are essential for flight planning, navigation, and ensuring aircraft safety during takeoff, landing, and flight operations.
- Renewable energy
Wind speed measurements play a critical role in site selection, turbine design, and power output optimization in the wind energy sector.
- Construction
Wind speed assessments are vital for assessing structural integrity, crane operations, and safety considerations in construction projects.
- Agriculture
Wind speed data are utilized in agriculture for applications such as crop spraying, ventilation management, and predicting weather patterns.