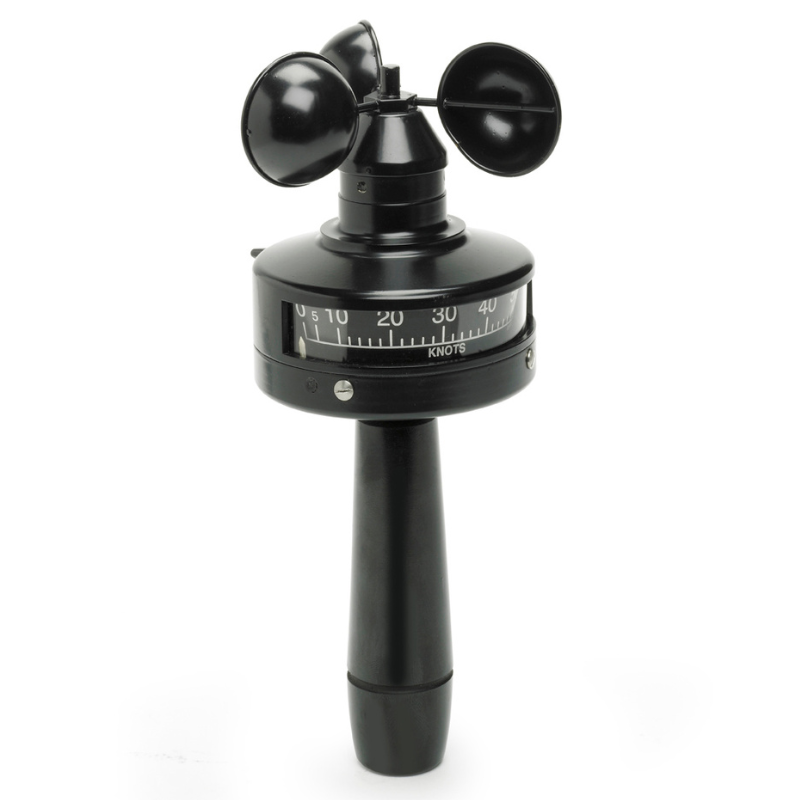
Cup anemometers stand as stalwart instruments, faithfully measuring wind speed. These devices have a rich history and continue to play a crucial role in various industries where wind assessment is vital.
A cup anemometer is a device used to measure wind speed. It typically consists of three or four cups mounted on horizontal arms that rotate around a vertical axis. As the wind blows, the cups rotate, and the speed of rotation is proportional to the wind speed.
Here’s what you need to know about cup anemometers:
- Principle of Operation: Cup anemometers work on the principle of drag force. When the wind blows, it exerts a force on the cups, causing them to rotate. The rotation speed is then measured to determine wind speed.
- Calibration: they need to be carefully calibrated to ensure accurate measurements. Calibration involves comparing the rotational speed of the cups with known wind speeds in a controlled environment.
- Accuracy: they are generally accurate for measuring wind speeds within their operational range. However, factors such as turbulence, instrument errors, and mounting height can affect accuracy.
- Mounting:they are typically mounted on poles or towers at a certain height above the ground to minimize interference from obstacles and to capture undisturbed wind flow.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to ensure the proper functioning of cup anemometers. This includes cleaning the cups, checking for any damage or wear, and verifying calibration.
- Applications: Used in meteorology, climate research, environmental monitoring, and various industries such as renewable energy (e.g., wind farms) and aviation (e.g., airports).
- Limitations: they have limitations, such as difficulty in measuring wind direction (they only measure speed) and susceptibility to errors in high winds due to mechanical limitations.
- Advancements: In recent years, technological advancements have led to the development of digital cup anemometers with enhanced accuracy, data logging capabilities, and remote monitoring options.
How Cup Anemometers Work
Cup anemometers operate on a straightforward principle: the rotation of cups in the wind generates angular momentum, which is then converted into wind speed measurements. However, factors such as friction, inertia, and wind flow patterns can affect their accuracy.
Types of Cup Anemometers
Over time, these wind speed meter designs have evolved, leading to various types catering to specific needs. Traditional three-cup designs remain prevalent, while modern iterations feature enhancements like digital displays and wireless connectivity.

Applications
The versatility extends across multiple domains. In Meteorological Equipment, they provide essential data for weather forecasting and climate studies. In aviation, they aid in assessing flight conditions. Moreover, in the renewable energy sector, they guide the placement and efficiency of wind turbines.
Advantages of Cup Anemometers
One of the primary advantages is their reliability. They offer consistent and accurate wind speed measurements over extended periods. Additionally, they are relatively simple to install and maintain, making them accessible to a wide range of users.